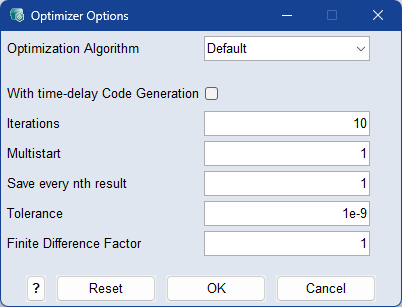
Optimizer Options
Optimization step > Configure
From the Optimization Algorithm drop-down list, select the optimization algorithm for which you want to customize the settings:
With time-delay Code Generation
When activated, C code is generated from the function and optimization works on compiled C code. This only works if the function does not use external models. This speeds up the optimization when the timeDelay method is used in the function, in other cases it's usually slower.
Iterations
Enter the maximum number of iterations to be performed during optimization.
Multistart
Enter the number of times to run the optimizer with different initial values.
If set to a number greater than one, the optimizer will run multiple times. The first optimization is started with the current working parameter set, while subsequent optimizations start with random parameter values. This can be used to find a global optimum.
Save every nth result
Save only every nth iteration as a temporary parameterset. Typical values are in the range [1, 100], default is 1.
Tolerance
The optimization stop criterion. Typical values range from 1e-9 to 1e-16.
The value is used to stop the optimization in the following cases:
-
A parameter change by the optimization algorithm would be smaller than this value.
-
The change in the cost function is smaller than this value. The optimization has converged.
Finite Difference Factor
The gradients of external models (FMU, …) are calculated by finite gradients.
Gradient = (f(x+e) - f(x)) / e
with e = Finite Difference Factor * Normalized Parameter Range * 1.5e-8
If the output of a model does not change by such a small value, the optimizer stops at the first iteration. In this case, the Finite Difference Factor must be increased. Typical values are 10, 100, 1000, 10,000,...
1.5e-8 is the square root of the smallest number that can be shown with a double precision floating point number. If the model uses single precision floating point numbers, set the factor to 10,000 to consider the loss of precision.
With time-delay Code Generation
When activated, C code is generated from the function and optimization works on compiled C code. This only works if the function does not use external models. This speeds up the optimization when the timeDelay method is used in the function, in other cases it's usually slower.
Iterations
Enter the maximum number of iterations to be performed during optimization.
Multistart
Enter the number of times to run the optimizer with different initial values.
If set to a number greater than one, the optimizer will run multiple times. The first optimization is started with the current working parameter set, while subsequent optimizations start with random parameter values. This can be used to find a global optimum.
Save every nth result
Save only every nth iteration as a temporary parameterset. Typical values are in the range [1, 100], default is 1.
Tolerance
The optimization stop criterion. Typical values range from 1e-9 to 1e-16.
The value is used to stop the optimization in the following cases:
-
A parameter change by the optimization algorithm would be smaller than this value.
-
The change in the cost function is smaller than this value. The optimization has converged.
Finite Difference Factor
The gradients of external models (FMU, …) are calculated by finite gradients.
Gradient = (f(x+e) - f(x)) / e
with e = Finite Difference Factor * Normalized Parameter Range * 1.5e-8
If the output of a model does not change by such a small value, the optimizer stops at the first iteration. In this case, the Finite Difference Factor must be increased. Typical values are 10, 100, 1000, 10,000,...
1.5e-8 is the square root of the smallest number that can be shown with a double precision floating point number. If the model uses single precision floating point numbers, set the factor to 10,000 to consider the loss of precision.
With time-delay Code Generation
When activated, C code is generated from the function and optimization works on compiled C code. This only works if the function does not use external models. This speeds up the optimization when the timeDelay method is used in the function, in other cases it's usually slower.
Iterations
Enter the maximum number of iterations to be performed during optimization.
Multistart
Enter the number of times to run the optimizer with different initial values.
If set to a number greater than one, the optimizer will run multiple times. The first optimization is started with the current working parameter set, while subsequent optimizations start with random parameter values. This can be used to find a global optimum.
Save every nth result
Save only every nth iteration as a temporary parameterset. Typical values are in the range [1, 100], default is 1.
Tolerance
The optimization stop criterion. Typical values range from 1e-9 to 1e-16.
The value is used to stop the optimization in the following cases:
-
A parameter change by the optimization algorithm would be smaller than this value.
-
The change in the cost function is smaller than this value. The optimization has converged.
With time-delay Code Generation
When activated, C code is generated from the function and optimization works on compiled C code. This only works if the function does not use external models. This speeds up the optimization when the timeDelay method is used in the function, in other cases it's usually slower.
Iterations
Enter the maximum number of iterations to be performed during optimization.
Multistart
Enter the number of times to run the optimizer with different initial values.
If set to a number greater than one, the optimizer will run multiple times. The first optimization is started with the current working parameter set, while subsequent optimizations start with random parameter values. This can be used to find a global optimum.
Save every nth result
Save only every nth iteration as a temporary parameterset. Typical values are in the range [1, 100], default is 1.
Tolerance
The optimization stop criterion. Typical values range from 1e-9 to 1e-16.
The value is used to stop the optimization in the following cases:
-
A parameter change by the optimization algorithm would be smaller than this value.
-
The change in the cost function is smaller than this value. The optimization has converged.
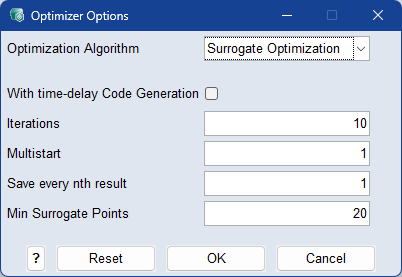
Min. Surrogate Points
The surrogate model is a radial basis function model, and the minimum number of basis functions used in the model is defined here. The initial model is assessed at the location of these basis functions.
With time-delay Code Generation
When activated, C code is generated from the function and optimization works on compiled C code. This only works if the function does not use external models. This speeds up the optimization when the timeDelay method is used in the function, in other cases it's usually slower.
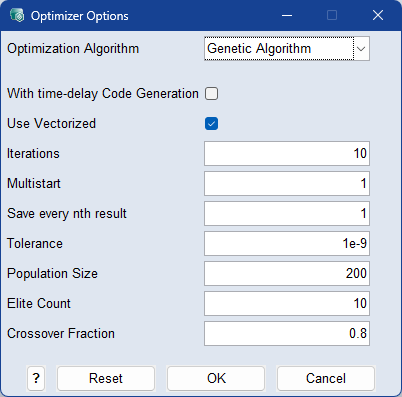
Use Vectorized
If activated, the MOCA function is evaluated with all candidate solutions in a single vectorized call. The function's memory usage increases by a factor proportional to the number of individuals in the population during the evaluation process.
Iterations
Enter the maximum number of iterations to be performed during optimization.
Multistart
Enter the number of times to run the optimizer with different initial values.
If set to a number greater than one, the optimizer will run multiple times. The first optimization is started with the current working parameter set, while subsequent optimizations start with random parameter values. This can be used to find a global optimum.
Tolerance
The optimization stop criterion. Typical values range from 1e-9 to 1e-16.
The value is used to stop the optimization in the following cases:
-
A parameter change by the optimization algorithm would be smaller than this value.
-
The change in the cost function is smaller than this value. The optimization has converged.
Population Size
The number of candidate solutions available during the optimization process. Increasing the population size may lead to better solutions, but also results in longer processing times and higher memory usage. The usual range for this value is between 100 and 1000.
Elite Count
The number of good candidate solutions that are carried over unchanged to the next iteration. Using a smaller number causes the algorithm to converge at a slower pace. Common values range from 5 to 20% of the overall population size.
Crossover Fraction
Crossover candidate solutions are produced by combining two candidates. Mutated candidate solutions are created by changing a candidate at random. The crossover fraction controls the amount of crossover and mutation, with a range of 0 to 1. A value of 0.8 means that 20% of candidates undergo mutation, while 80% are produced by crossover. Typically, values range from 0.5 to 0.9.
With time-delay Code Generation
When activated, C code is generated from the function and optimization works on compiled C code. This only works if the function does not use external models. This speeds up the optimization when the timeDelay method is used in the function, in other cases it's usually slower.
Iterations
Enter the maximum number of iterations to be performed during optimization.
Multistart
Enter the number of times to run the optimizer with different initial values.
If set to a number greater than one, the optimizer will run multiple times. The first optimization is started with the current working parameter set, while subsequent optimizations start with random parameter values. This can be used to find a global optimum.
Save every nth result
Save only every nth iteration as a temporary parameterset. Typical values are in the range [1, 100], default is 1.
Tolerance
The optimization stop criterion. Typical values range from 1e-9 to 1e-16.
The value is used to stop the optimization in the following cases:
-
A parameter change by the optimization algorithm would be smaller than this value.
-
The change in the cost function is smaller than this value. The optimization has converged.
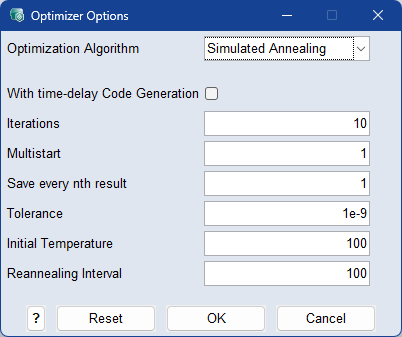
Initial Temperature
This value controls the probability of accepting worse solutions during the optimization process. Typical values range from 50 to 200.
The initial temperature decreases by Initial Temperature * 0.95Iterations per iteration. As the temperature decreases, the probability of accepting worse solutions decreases.
Reannealing Interval
After this number of iterations, the temperature is increased. Typical values are 50 to 200.
With time-delay Code Generation
When activated, C code is generated from the function and optimization works on compiled C code. This only works if the function does not use external models. This speeds up the optimization when the timeDelay method is used in the function, in other cases it's usually slower.
Iterations
Enter the maximum number of iterations to be performed during optimization.
Multistart
Enter the number of times to run the optimizer with different initial values.
If set to a number greater than one, the optimizer will run multiple times. The first optimization is started with the current working parameter set, while subsequent optimizations start with random parameter values. This can be used to find a global optimum.
Save every nth result
Save only every nth iteration as a temporary parameterset. Typical values are in the range [1, 100], default is 1.
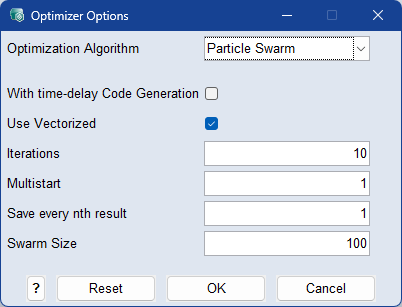
Swarm Size
The number of candidate solutions available during the optimization process. Enlarging the swarm size leads to longer optimization duration and increased memory usage, but may lead to better solutions. Typical values range from 50 to 200.
For an explanation of the optimization algorithms, see Optimization Algorithms