Configure Automatic Feature Selection <output>
Model menu > NARX Feature Search > Configure
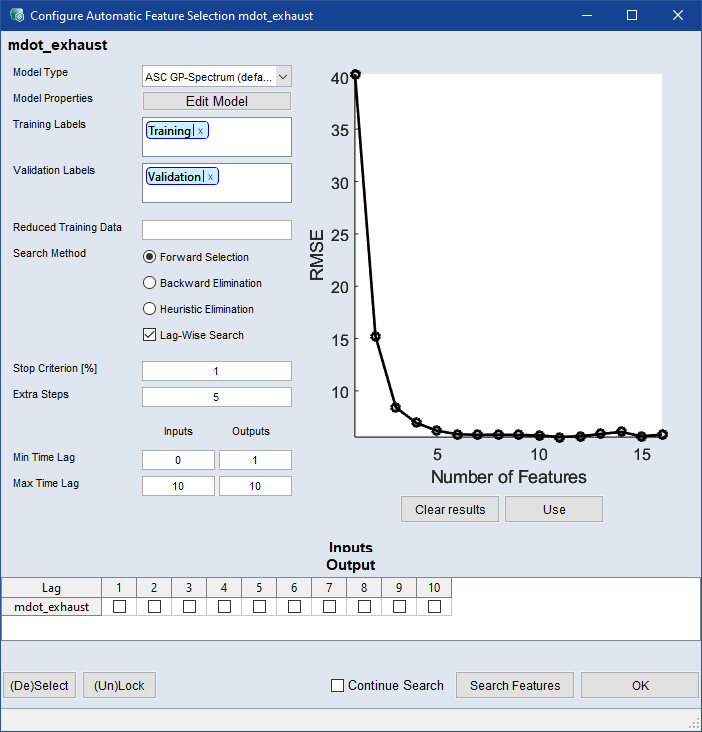
The  Configure Automatic Feature Selection <output> window for the NARX structure modeling method contains the following elements.
Configure Automatic Feature Selection <output> window for the NARX structure modeling method contains the following elements.
Model Type
Select the NARX model type you want to use for Automatic Feature Selection.
For best results, the chosen algorithm should be the same one that will be used in the actual model training later. See also NARX Model Types.

Click to edit the parameters of the model. See NARX Model Types for a description of the model parameters.
Training Labels
Assign the labels you want to train the model on. If you use multiple labels, all data associated with at least one of the labels is used.
Assign a label by double-clicking the field and typing the name. Select the dataset from the list of suggestions.
Use the x on the label or Del to remove the label.
Validation Labels
Assign the labels of the data you want to use as validation data. If you use multiple labels, all data associated with at least one of the labels is used.
Assign a label by double-clicking the field and typing the name. Select the dataset from the list of suggestions.
Use the x on the label or Del to remove the label.
|
Note |
|---|
|
If the validation labels are not assigned to any data, the model is trained without validation. A message appears in the log window. You can assign labels to data in the Manage Datasets window. |
Reduce Training Data
Intelligent training data selection (farthest first heuristic). Enter the number of reduced training data points if you want to use only a reduced set of training data.
Search Method
-
Forward Selection
Starts with an empty feature set and iteratively adds the feature that gives the maximum increase in model quality. Recommended setting for faster convergence.
-
Backward Elimination
Uses all features at the beginning and iteratively removes the feature with the least impact on the model. The advantage of backward selection is that it identifies interdependencies between features.
-
Heuristic Elimination
Uses all features in the beginning and iteratively removes the feature with the least impact on the model based on heuristic input relevance. This is a faster method (compared to the other methods, especially Backward Elimination) to automatically find the NARX structure.
-
Lag-Wise Search
When this checkbox is active, the inputs are searched lag-wise. This speeds up the feature search.
Stop Criterion [%]
Stopping criterion for automatic feature selection.
The search stops when the quality of the model, measured as the root mean square error (RMSE) on the training data, cannot be increased further (Forward Selection) or becomes worse (Backward Elimination) than the specified stopping value.
Extra Steps
This value is only reset if the current NARX structure provides less RMSE than the best structure found previously.
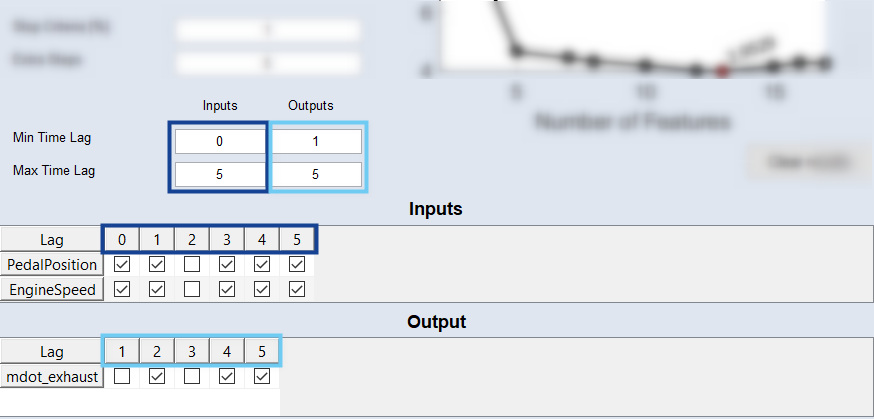
Min Time Lag and Max Time Lag
Minimum/maximum time lag for inputs and outputs of the NARX structure (see Feedback Structure).
Plot area
Shows RMSE vs. the number of features.

Click to clear the plot area.

Click to use the currently selected model configuration. You must first perform a Feature Search.
Inputs and Output tables
The Inputs table contains one row for each input. The Output table contains one row for the output you are currently working on.
Each  table contains one column for each possible time lag. An activated checkbox in a table cell means that the feature is selected.
table contains one column for each possible time lag. An activated checkbox in a table cell means that the feature is selected.

Selects/deselects all features in the selected cells or rows.

Locks/unlocks the selected cells or rows. The state of the corresponding features remains unchanged during a subsequent feature search. When you apply the selections, the locked cells are also locked in the Model Configurations: NARX Structure
Locked cells have a gray background.
Continue Search
Locks the currently selected features and continues the search with the currently unselected features.

Starts the feature search. The plot is updated during the feature search.

Applies the setting and transfers the results to the NARX Feature Search window.
See also
Model Configurations (ASCMO-DYNAMIC)