Global Optimization
Optimization menu > Global Optimization
For a global optimization, the optimization is performed at all operating points at the same time (not successively like the Single Criteria Optimization which goes through all operating points in succession in batch mode).
This enables two additional items:
- Consideration of the smoothness of the maps (steepness/gradient of the maps)
- Observation of total values for driving cycles with a weighting with respect to the duration of stay at the operating points (see Calibration > Prognosis)
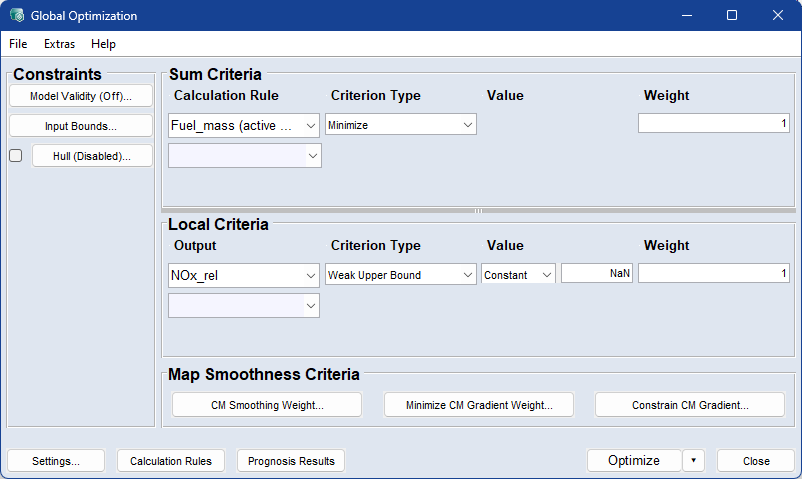
In the Global Optimization window, the necessary criteria and values can be set.
The Global Optimization window contains the following elements:
Constraints
-
Model Validity
Opens the Valid Model Range window. In that window, you can restrict optimization of each criterion to the respective valid model range.
Note
The valid mode range makes the optimization slow and no solution might be found at all, because the valid regions are not contiguous.
In many cases it is better to constrain the solutions to the Input Bounds > Fit all Bounds to Data, see next constraint option.
-
Input Bounds
Opens the Input Bounds window where you can define the range to be considered for the modeling for each input.
-
Checkbox and
Hull (*)
If the checkbox is enabled, the button is named Hull (2D). Otherwise, the button is named Hull (Disabled).
The button opens the Configure Convex Hull on Inputs window where you can configure 2D, 3D, and/or 4D hulls.
Note
You must activate the checkbox manually even if you clicked Hull (Disabled) and configured hulls.
Minimize or maximize the prognosis.
-
Calculation Rule column
The drop-down lists in this column offer all outputs for selection. In addition, the Remove entry can be used to delete a row.
-
Criterion Type column
The optimizing criterion for the respective output. Available selections are:
Minimize/Maximize
A target value which should be reached as closely as possible.
Hard Upper Bound
Hard upper limit value for the optimizing goal.
Weak Upper Bound
Weak upper limit.
See also Optimization Criteria.
-
Value column
Input field for the value of the bound. Not available for the Minimize and Maximize criterion types.
-
Weight column
The weighting of the output for the optimization with respect to several outputs. Not available for the Hard Upper Bound criterion type.
The weights of the different criteria are normalized. See the
 example.
example.
-
Output column
The drop-down lists in this column offer all outputs for selection. In addition, the Remove entry can be used to delete a row.
-
Criterion Type column
Here, you select the optimizing criterion for the respective output. Available selections are:
Weak Upper/Lower Bound
Weak upper or lower limit.
Target
A target value which should be reached as closely as possible.
Hard Upper/Lower Bound
Hard upper or lower limit value for the optimizing goal.
See also Optimization Criteria.
-
Value columns
In the first Value column, the value can be set as global (Constant) or per OP.
The content of the second Value column depends on the selection in the first column.
selection in 1st "value" column
content of 2nd "Value" column
Constant
Input field for the value of the constant target or bound.
per OP
Map button, which opens the Optimization Output Constraint (<i>) Output <output> window.
In that window, you define a map with optimization targets or bounds for each operating point.
-
Weight column
The weighting of the output for the optimization with respect to several outputs. Not available for the Hard Upper/Lower Bound criterion types.
Since the smoothing of maps is generally in contradiction to the other requirements, a weighting can be specified here. ).
Map Smoothness Criteria
-
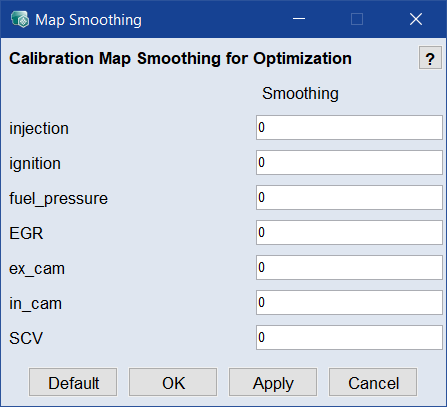
CM Smoothing Weight
Opens the
 Map Smoothing window where you can define the smoothness for the resulting calibration maps. A value of 0 means no smoothing, a value of 1 means strong smoothing.
Map Smoothing window where you can define the smoothness for the resulting calibration maps. A value of 0 means no smoothing, a value of 1 means strong smoothing. -
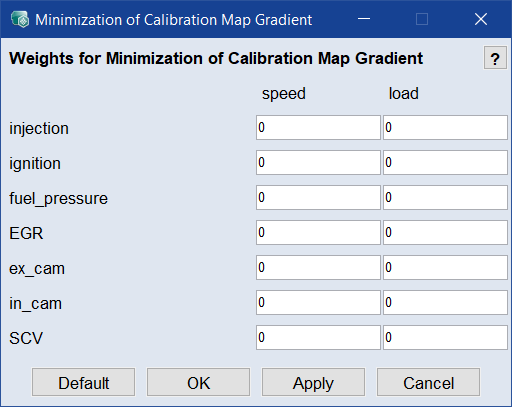
Minimize CM Gradient Weight
Opens the
 Minimization of Calibration Map Gradient window where you can assign weights for the minimization of calibration map gradients. Meaningful weights depend on several criteria; they are usually in the range 10-5 - 105. A value of 0 means no gradient minimization.
Minimization of Calibration Map Gradient window where you can assign weights for the minimization of calibration map gradients. Meaningful weights depend on several criteria; they are usually in the range 10-5 - 105. A value of 0 means no gradient minimization. -
Constrain CM Gradient
Opens the Limitation of Calibration Map Gradient window where you can constrain the gradients of the calibration maps individually for each input.
Note
When optimizing an OP list, the gradient constraints apply only to the gradients between the individual OPs, but not necessarily to the whole underlying grid of the corresponding calibration map.
When optimizing over a driving cycle, the gradient constraints apply to the grids of the corresponding calibration maps.

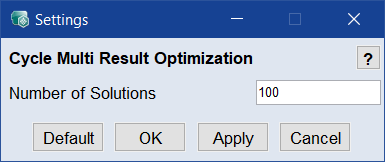
Opens the Settings window for global optimization.

Opens the Calculation Rules for Prognosis window.

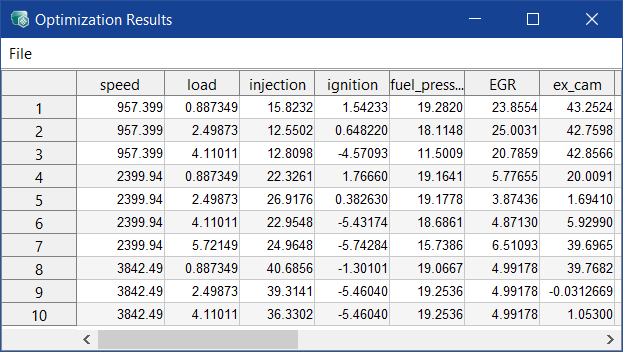
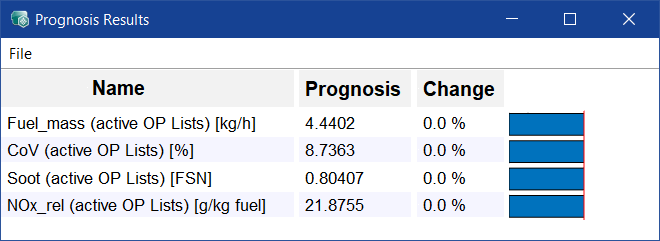
Opens the  Prognosis Results window where the effects of changes in the prognosis parameters and/or maps on outputs are displayed.
Prognosis Results window where the effects of changes in the prognosis parameters and/or maps on outputs are displayed.

Performs the optimization on the currently (in the ISP view) set operating point.
|
Note |
|---|
|
If the optimization cannot be executed, because of unrealizable criteria and restrictions, the optimization finishes providing further information in the log window. |
Results are displayed in the log window, and calculated values appear in the ISP view.
Use  for further options:
for further options:
Export Job to Docker: Exports the single result optimization information as *.docker.ascmo file. Use the file to perform the optimization in a Docker container, e.g., in the cloud.

Closes the window without starting an optimization. Changed settings are kept.
See also
Settings (Global Optimization)