Defining Calculated Signals
For a general overview of the window, see Calculated Signals.
The following steps describe the drag and drop usage. It is also possible to directly type into the formula editor field, and a drop-down list offers the available signals or mathematical operators.
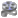 Creating Calculated Signals.
Creating Calculated Signals.
-
If this is the first calculated signal to be defined, you can directly start with step 2. If you have already defined a calculated signal, click
 .
.By default, the name of the new calculated signal is set to "CalculatedSignal". If this name is already in use, it is extended by an increasing number.
-
In the Name field, you can enter another name instead of the default name.
Note
Valid characters are a-z, A-Z, 0-9, underscore, point, and square brackets. Square brackets must always occur in pairs. Other characters or blank space are not allowed.
-
Optionally, you can enter a unit in the Unit field.
-
Drag and drop one or more input signals into the Formula Definition field.
Note that enumeration signals can be used as input signals only in combination with the following functions:
- Raw() function for mathematical calculations using the decimal implementation value
- ToString() function for comparing the strings of different enumeration signals.
For each input signal, the file identifier and the short name of the signal are displayed. If several signals with the same short name exist, information about the device and/or the raster is additionally displayed to distinguish the signals.
If an input signal contains an error or warning, a corresponding icon is displayed in front of the file identifier. Note that you can save a calculated signal even if an input signal contains an error.
-
Connect the signals with mathematical operators.
You can drag a mathematical operator from the Toolbox field into the Formula Definition field. The Help field displays additional information about the meaning and usage of the operator.
Tip: To quickly navigate through the formula, use the keyboard buttons.
-
Open the Output Options and define the following parameters:
-
Rate: Define the rate in which a new sample
 Individual value of a signal measured at a certain time stamp. of the calculated signal shall be created.
Individual value of a signal measured at a certain time stamp. of the calculated signal shall be created.-
Combined Raster (Merge Raster) (by default): For every new sample of any input signal, a new sample for the calculated signal is created. This means, different input signal time rasters
 Time interval between the individual samples, given in ms. are merged.
Time interval between the individual samples, given in ms. are merged. -
Fixed: The calculation of a new sample is done in a periodic raster independently from the rasters of the input signals.
-
Same as Signal: The calculated signal has the same time stamps as the selected input signal. You can only select available input signals. Thus, for example, if the selected input signal has been deleted from the configuration, an error message is displayed.
-
-
Type: Select the data type of the calculated signal. A time offset is applied to the result of calculation only. It can be a negative or positive value with up to 6 decimals. A time offset allows to shift individual signals and thus synchronizes their time line with other signals from the same measure file.
-
Automatic (by default): The program tries to detect whether the result is a logical (Boolean) signal or not.
-
Boolean
-
Double
-
-
Time Offset for the calculated signal.
-
-
Click Save.
If the calculation is not valid, you cannot save the calculated signal. An error message is displayed and the exact location of the error is highlighted. After saving, the new calculated signal is available in the Variable Explorer and in the calculated signal list.
- To use the calculated signal, drag and drop it onto an instrument. For calculated signals, a square root symbol is shown as file identifier.
|
Note |
|---|
|
The copy and paste function is currently not supported in the Formula Definition field. |
See also