Dimensionality Reduction
Reducing the number of feedback values (features) can increase model quality and accelerate model training.
Several options are available in the Model properties window (Model Configurations window).
-
None: Use all features in the NARX structure in accordance with the set maximum time lags. This is sufficient for the diesel example.
-
Feature Extraction (PCA): Reduces the dimensionality of the feedback structure to the given number of features using a principle component analysis (PCA).
Note
In many cases, not all features of the feedback structure are necessary, e.g. due to redundancies. A smaller number of features supports faster model training.
-
Automatic Feature Selection: As an alternative to manual feature selection, you can find the proper feature setting via an automatic search.
-
Manual: Manual feature selection allows the user the explicit selection of the feature set by activating the corresponding checkboxes in the Inputs and Output table (in Model Configurations window).
This is recommended either when the model training with Dimensionality Reduction None yields insufficient model quality or when the system-specific time dependencies are known.
Use Automatic Feature Selection
|
Note |
|---|
|
In the case of more than one system output, this procedure has to be performed individually for each output. |
-
Select Model > NARX Feature Search > Configure.
-
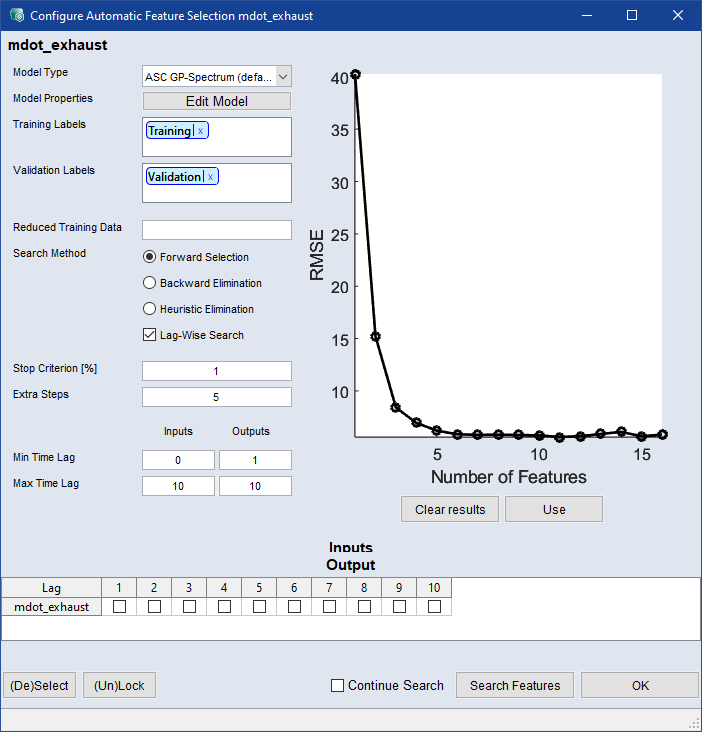
-
In the Model Type drop-down, select a model type you want to use for Automatic Feature Selection.
For best results, the selected type should be the same as in the actual model training.
-
If desired, click Edit Model to open the <output> - Parameters window ( Model Training) and edit the model parameters.
-
In the Search Method area, activate the option for the method you want to use.
-
Forward Selection
Starts with an empty feature set and iteratively adds the feature that gives the maximum increase in model quality. Recommended setting for faster convergence.
-
Backward Elimination
Uses all features at the beginning and iteratively removes the feature with the least impact on the model. The advantage of backward selection is that it identifies interdependencies between features.
-
Heuristic Elimination
Uses all features in the beginning and iteratively removes the feature with the least impact on the model based on heuristic input relevance. This is a faster method (compared to the other methods, especially Backward Elimination) to automatically find the NARX structure.
-
Lag-Wise Search
When this checkbox is active, the inputs are searched lag-wise. This speeds up the feature search.
-
In the Stop Criteria [%] field, enter a value.
The search stops if the model quality cannot be increased further (Forward Selection) or becomes worse (Backward Elimination) than the given stopping value.
-
In the Min Time Lag and Max Time Lag fields, enter the minimum and maximum time lags for inputs and outputs.
-
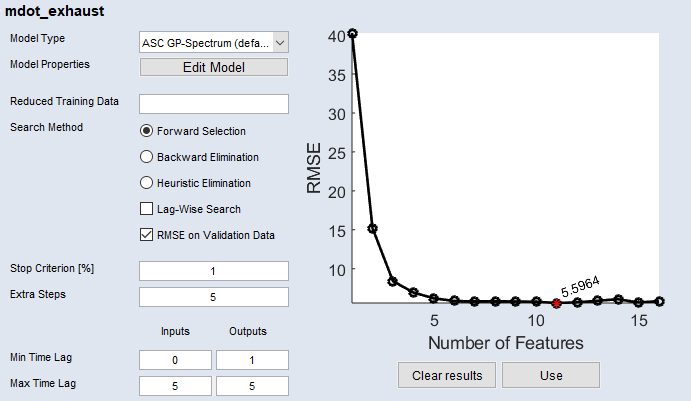
Click Search Features to start automatic feature selection. The search may take some time. Progress is shown in the plot on the top right of the Automatic Feature Selection <output> window.
When the search is complete, the best result is marked.
-
Click Apply to apply the result.
When you have selected features for all outputs, you can return to the Model Properties window and start model training with the OK button.