Variables RMSE and R2
A series of variables is used for quantifying the function quality. These variables are described in this section.
RMSE (Root Mean Squared Error)
The RMSE describes the variance to be expected (standard deviation) about the model: A second measurement falls less than 1 RMSE from the model prediction with a probability of 68% (with 95.5% < 2 RMSE, 99.7% < 3 RMSE, etc.).
The RMSE is defined as follows:
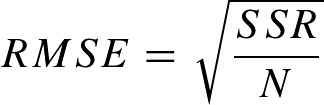
Equ. 1: Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE)
whereby N = the number of measuring data and

Equ. 2: Sum of Squared Residuals (SSR)
Therefore, SSR is the sum of squared residuals (SSR = Sum of Squared Residuals).
Coefficient of Determination R2
The coefficient of determination R2 is derived from the comparison of the variance that remains after the model training (SSR) with the variance concerning the mean value of all measuring data (SST)
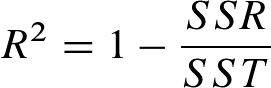
Equ. 3: Coefficient of determination R2 whereby
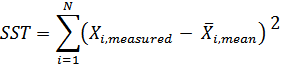
Equ. 4: Total Sum of Squares (SST)
R2 is a relative measure for evaluating the function output error – it indicates which portion of the total variance of the measuring data is described by the function.